Botox treatment
 The use of botulinum toxin is approved for the treatment of tension headaches and chronic migraine. The PREEMPT study 4 showed that this treatment can be sufficiently effective. "The therapy with botulinum toxin can halve the number of days of pain (...) in many patients. Only in patients in whom the therapy fails or is not sufficiently effective, the significantly more cost-intensive antibodies therapy is indicated and also absorbed by the statutory health funds" explained Prof. Diener [Article...] This treatment can also be helpful for cluster headaches, but has as yet not been approved for this indication.
The use of botulinum toxin is approved for the treatment of tension headaches and chronic migraine. The PREEMPT study 4 showed that this treatment can be sufficiently effective. "The therapy with botulinum toxin can halve the number of days of pain (...) in many patients. Only in patients in whom the therapy fails or is not sufficiently effective, the significantly more cost-intensive antibodies therapy is indicated and also absorbed by the statutory health funds" explained Prof. Diener [Article...] This treatment can also be helpful for cluster headaches, but has as yet not been approved for this indication.
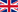
Botulinum toxin has been used as an approved drug in neurology since the 1980s, primarily in the treatment of specific movement disorders, the so-called focal dystonia. Such disorders include blepharospasm (eyelid spasm), oromandibular dystonia (mouth spasm, tongue spasm, pharyngospasm), spasmodic torticollis (wry neck), and other cervical dystonias. Furthermore, focal symptoms of segmental or secondary dystonias and spasticity can also be treated with botulinum toxin.
These include, for example, hemifacial spasm, movement disorders following a peripheral affection of the facial nerve, as well as certain spastic syndromes in adults and children, for instance, spastic drop foot, patients with cerebral palsy, spasticity of the arm after a stroke or spasticity of the hand and wrist after a stroke. For these indications, it is always injected in an intramuscular or subcutaneous manner. There is a treatment success rate of about 90% for eyelid spasm, and between 60 and 80% for torticollis, with improvement to temporary loss of symptoms.
Other applications:
- reduction of hyperhydrosis (excessive sweating),
- increased salivation (e. g. in patients with Parkinson's disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.